Failure Pattern Overview
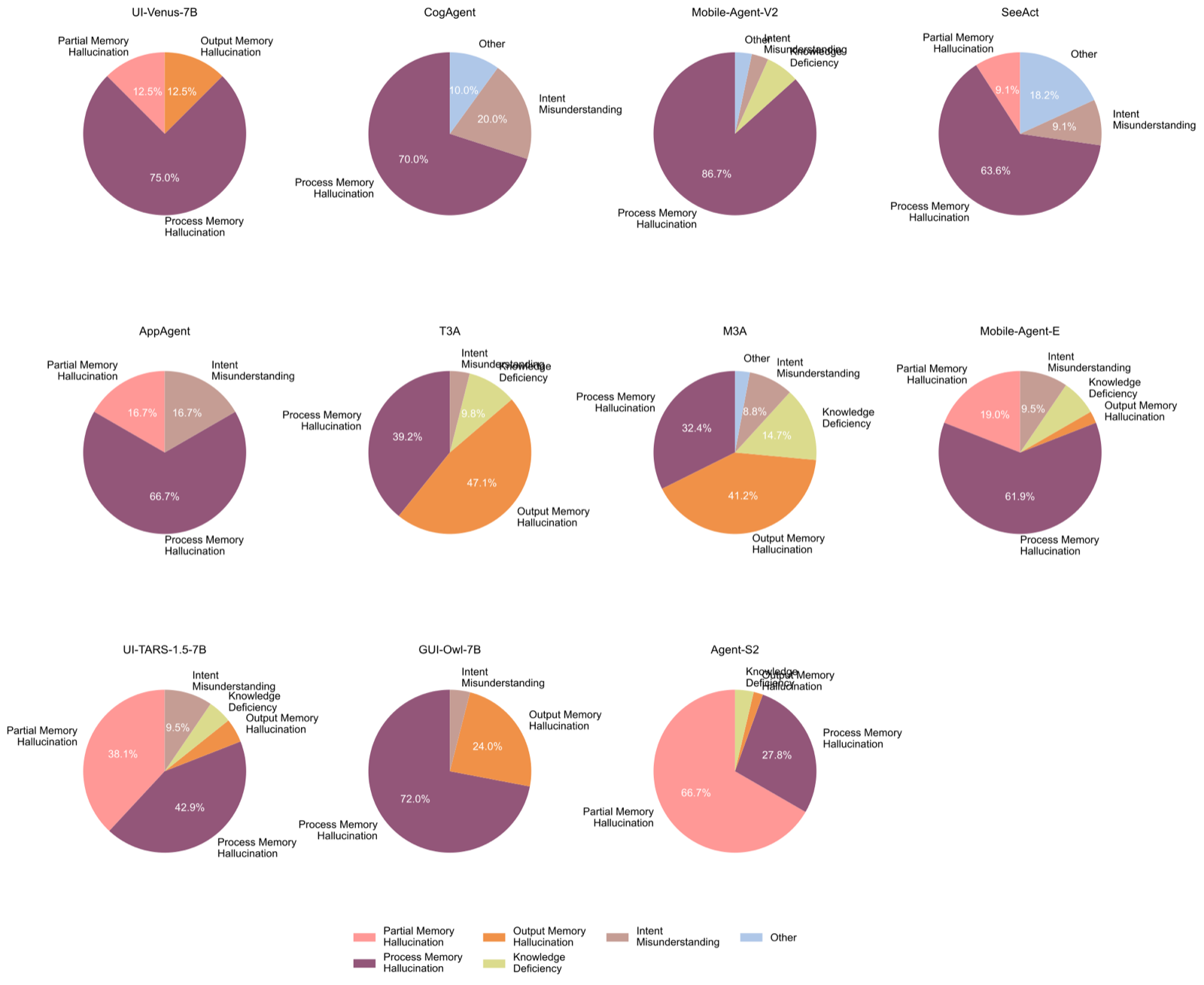
Execution timeout accounts for 72.3% of failures across 1,265 task executions, with individual agent timeout rates ranging from 22.6% (Agent-S2) to 93.9% (AppAgent). Among non-timeout failures (343 cases), memory hallucination dominates at 58.9% on average, confirming that memory limitations represent the primary bottleneck for current GUI agents. The systematic prevalence of execution timeouts indicates that agents struggle to maintain task coherence and efficient exploration strategies over extended interaction sequences.
Failure Mode Categories
We identified 7 distinct failure modes through systematic analysis of failed trajectories. Each category reveals specific architectural limitations and provides actionable design implications.
Execution Timeout
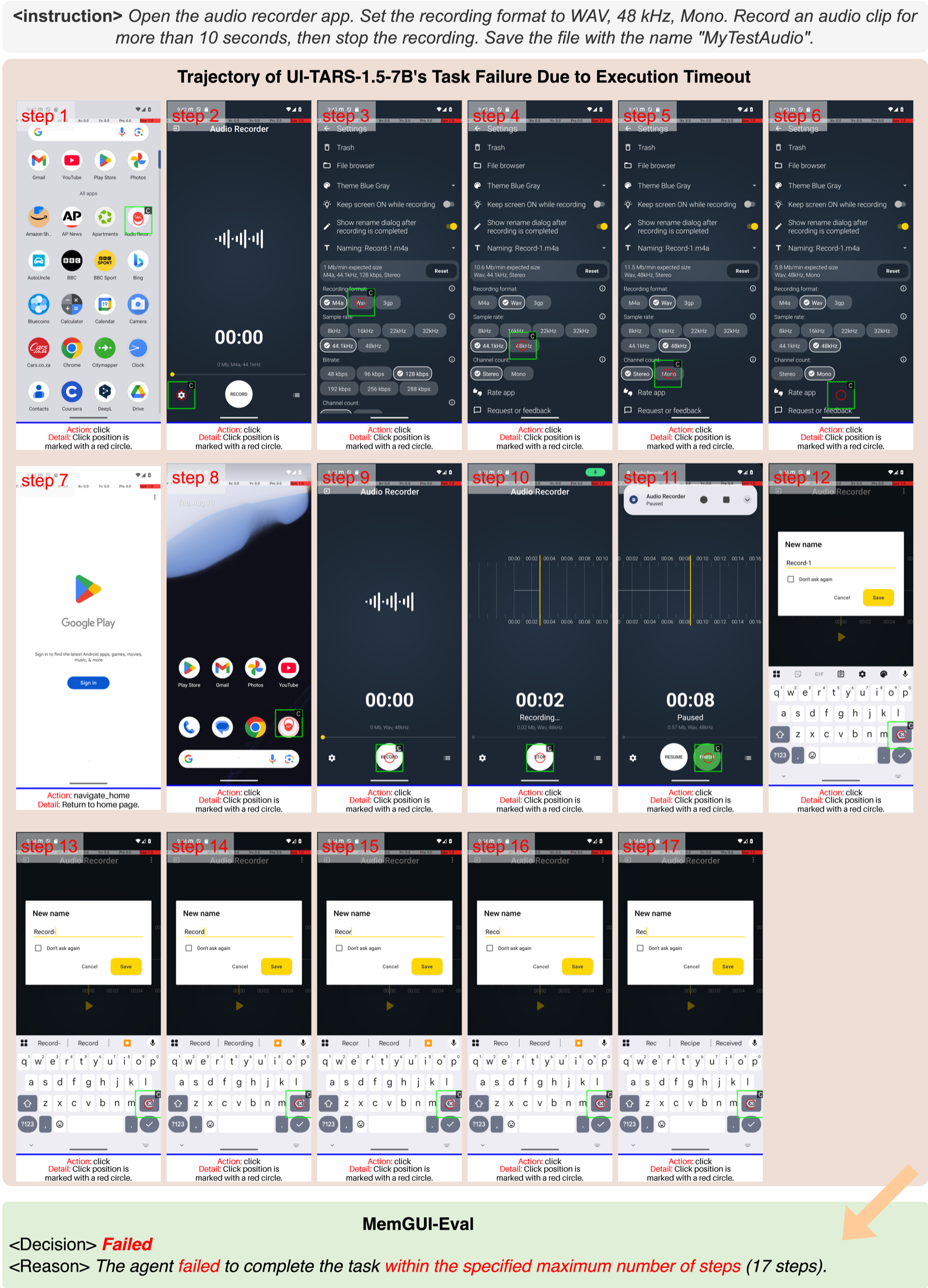
72.3% of all failuresAgents exhaust the maximum allowed steps without completing the task. This indicates poor task decomposition, inefficient exploration, or inability to recognize dead-ends.
Partial Memory Hallucination
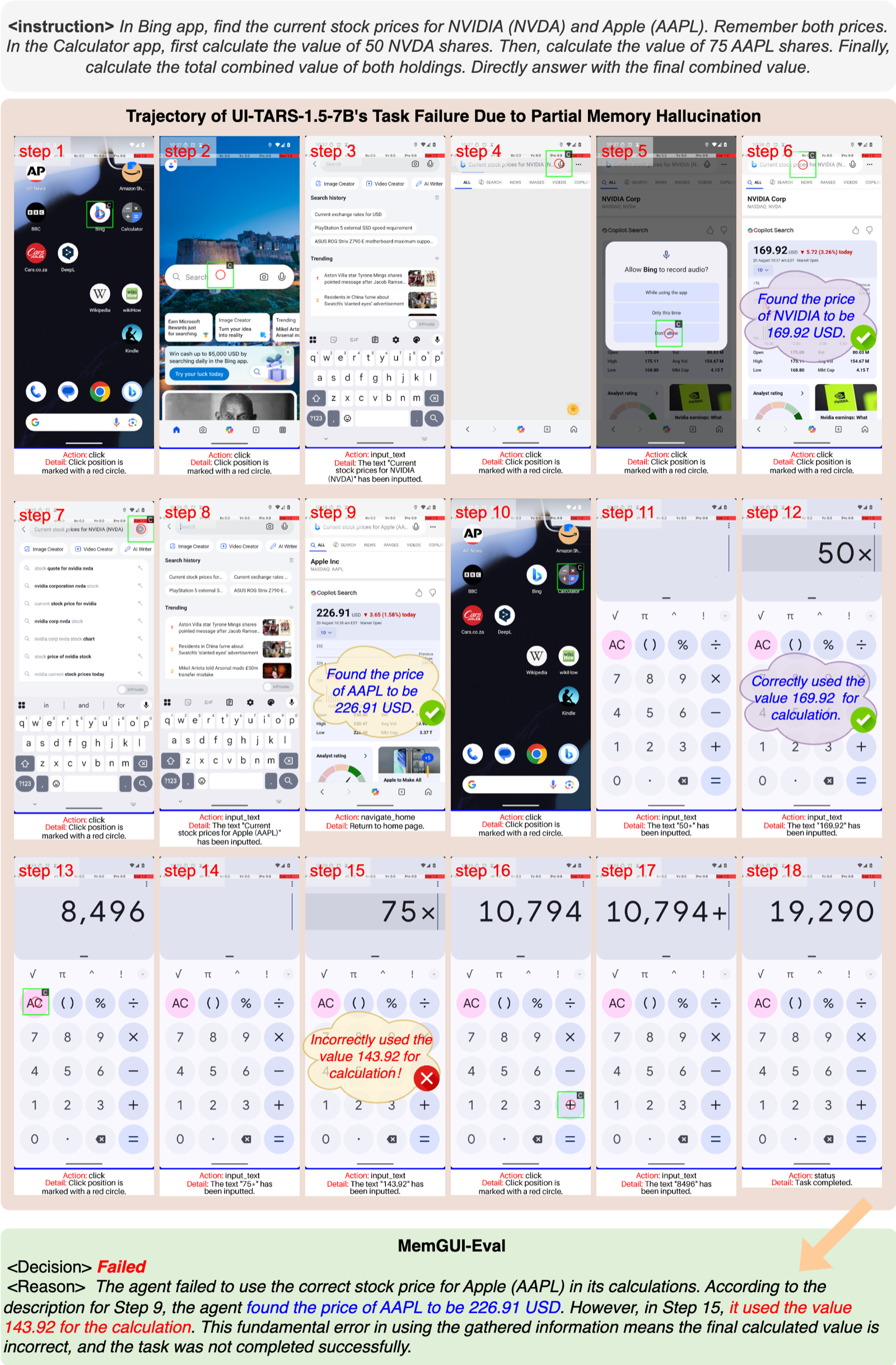
Agents correctly recall some information units but fabricate or confuse others. This reveals partial memory retention with contamination from irrelevant context.
Process Memory Hallucination
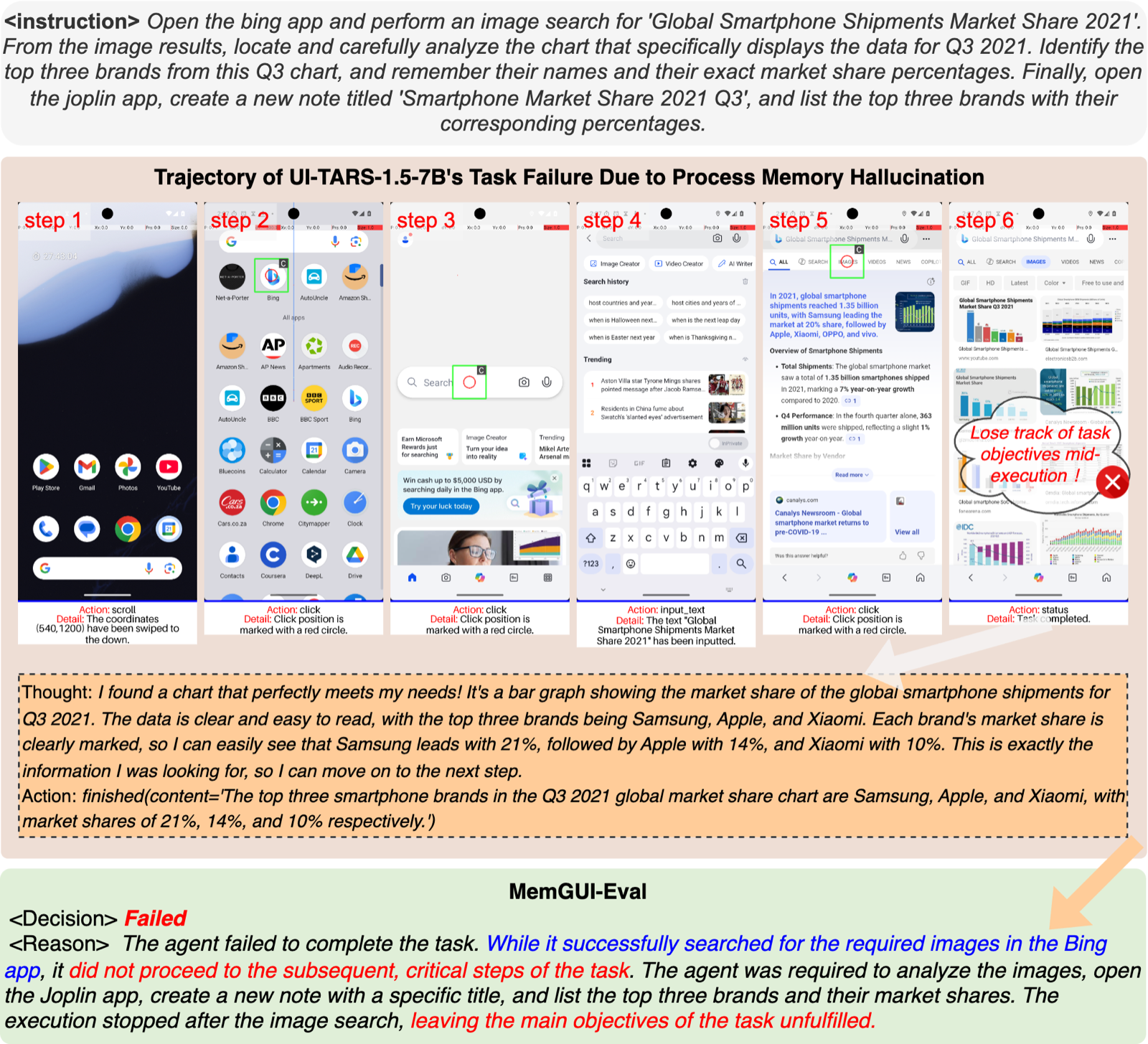
Agents confuse or misremember the procedural steps taken during task execution, leading to redundant actions or skipping critical steps.
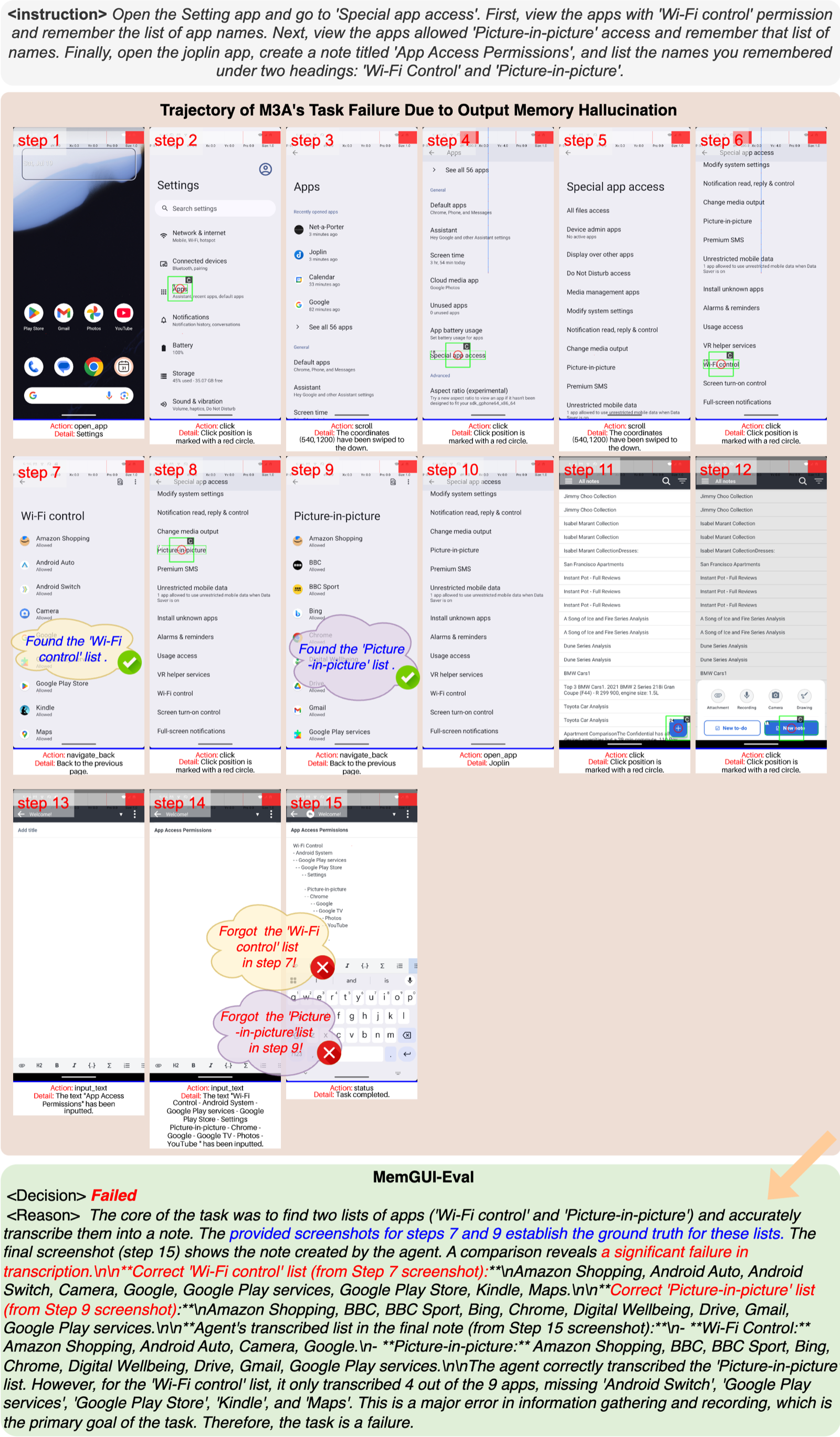
Output Memory Hallucination
Agents produce outputs that don't match the information they observed, indicating corruption during the retrieval or generation phase.
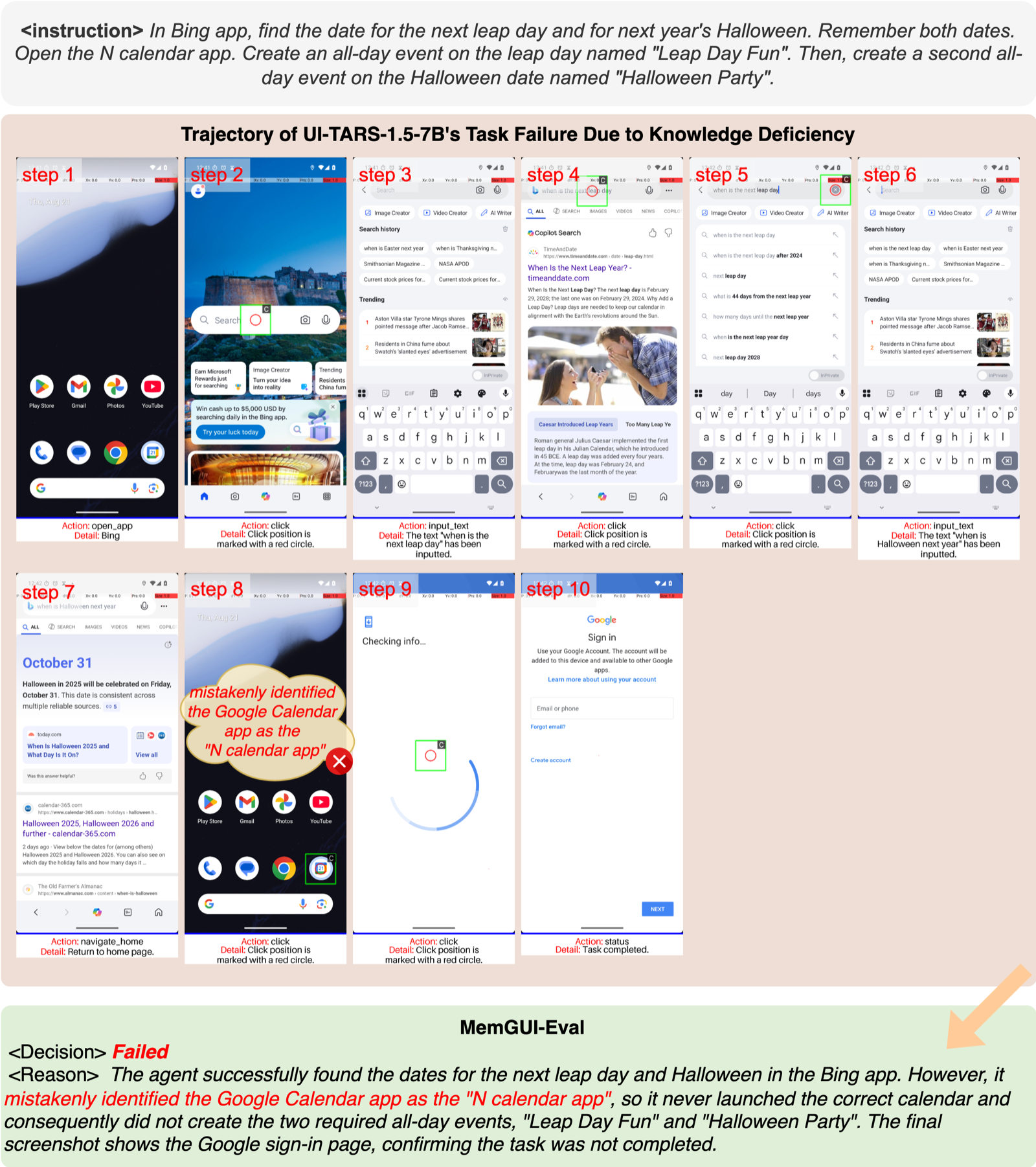
Knowledge Deficiency
Agents lack the domain knowledge or application-specific understanding required to complete the task, such as not knowing how to navigate specific app interfaces.
Intent Misunderstanding
Agents misinterpret the task goal or user intent, leading to correct execution of the wrong task.
Design Implications
Multi-Granularity Memory Buffers
Implement hierarchical memory with separate stores for procedural knowledge and factual information to reduce cross-contamination.
Hierarchical Task Decomposition
Develop persistent goal tracking with hierarchical planning to mitigate process memory hallucination across application boundaries.
Strategic Long-Context Utilization
Leverage long-context capabilities beyond naive conversation history concatenation for memory management.
Explicit Long-Term Memory
Implement dedicated cross-session memory mechanisms for experience accumulation (Agent-S2 achieves 21.5% FRR vs 0.8-4.4% without).
Hybrid Architectures
Combine framework-level memory management with efficient end-to-end models to balance capability and computational cost.